If you have been part of the Windows ecosystem for some time, the Task Manager most definitely would be something you are most familiar with.
Although many users know of its existence, only a few are well versed in the benefits it offers.
The interface of the Task Manager in Windows 10 is quite similar to its peer in Windows 8. The main purpose of the Task Manager is to make it easier for you to take control of applications running on the computer and to diagnose and optimise system performance.
Most users go for the method of hitting the Ctrl + Alt + Delete keys combination on their keyboard and then selecting Task Manager from the next screen to launch the Task Manager. However, a more quick and direct method to get there is to press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys. Other methods include launching it from the search bar or right-clicking on an empty space on the Windows taskbar and selecting Task Manager from the popup menu. The Task Manager window contains several tabs to navigate to different areas of functionality. We’ll take a brief look at all of these tabs in the lines below.
Processes
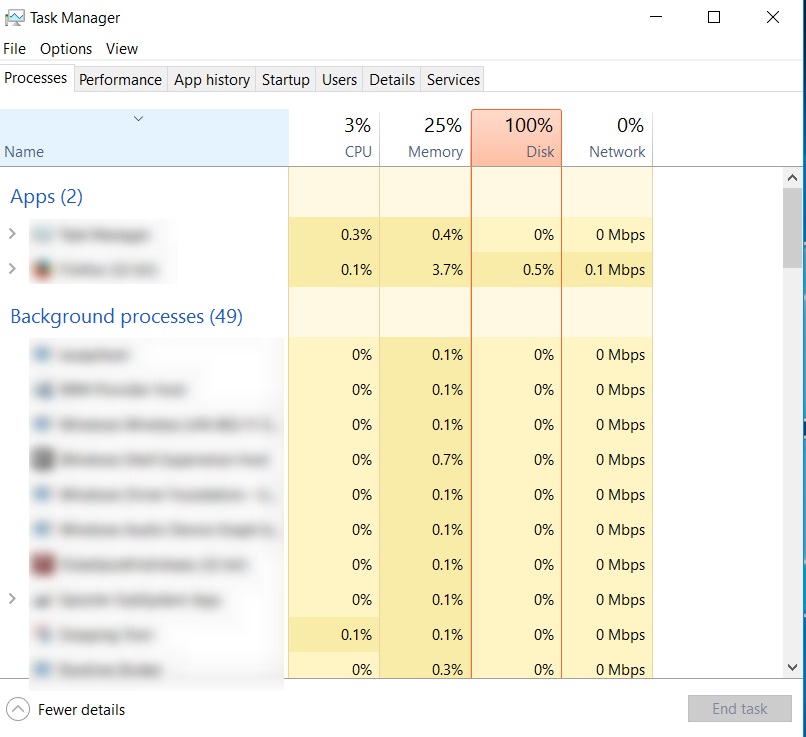
In this tab, all the programs and applications which are currently loaded are categorized into Apps, Background processes and Windows processes. The resources being utilized by each process are shown and can be sorted in ascending or descending order by clicking on the labels at the top of the respective column. The quantum of each resource being tied up by the concerning entity (highlighted in yellow) would increase depending on the usage. It would turn to orange and then red if resource utilization is high. Right-clicking on a single process opens a popup menu which gives you the ability to expand the process, and most importantly to end the process by selecting End task. You can also perform the latter by selecting a process and clicking End task on the bottom right corner of the screen. This has got to be easily the most important of all the functions available under this tab.
Performance
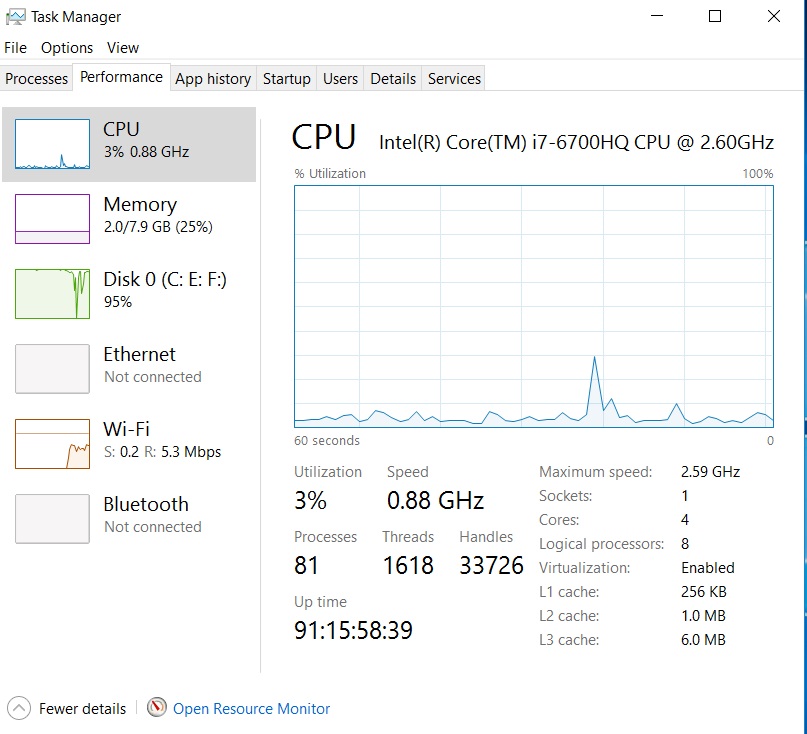
This tab gives you a view of the current performance of the CPU, Memory, Disk, Ethernet, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Easy to read graphs and values help the user to quickly comprehend the overall situation. If you require specific information on each component, this can be accomplished easily by clicking the respective label on the left. The resultant section will also provide detailed info on the section you just selected. The right-click menu will throw up a few more options, mainly concerned with changing the view. Also, the Resource Monitor can be launched from this tab.
App history
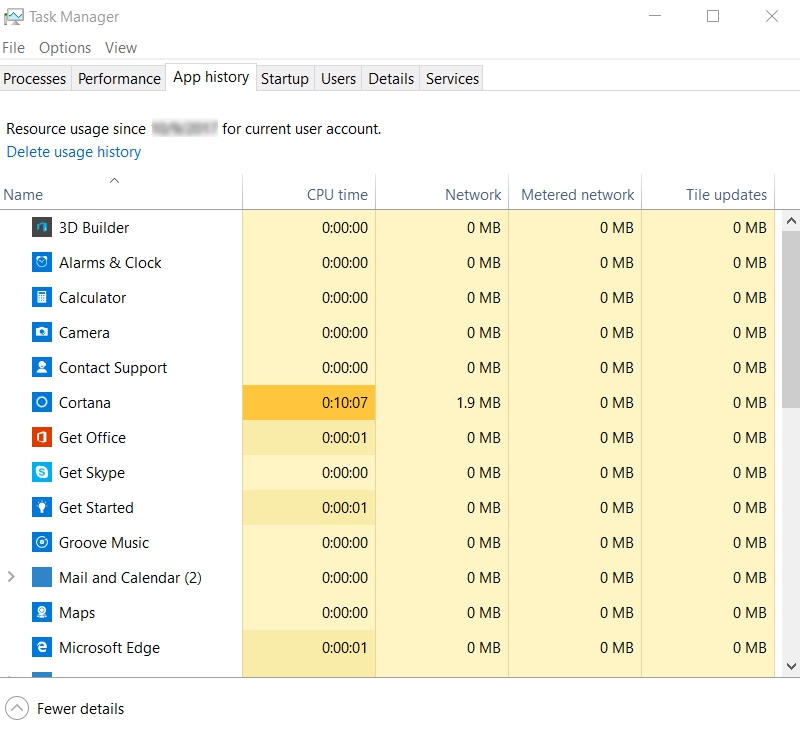
This tab provides a historical representation of the resource utilization of your PC. The usage shown in this tab is from the date mentioned at the top. This can be reset by clicking on Delete usage history. The App history tab is great for identifying applications that take up a significant amount of resources.
Startup
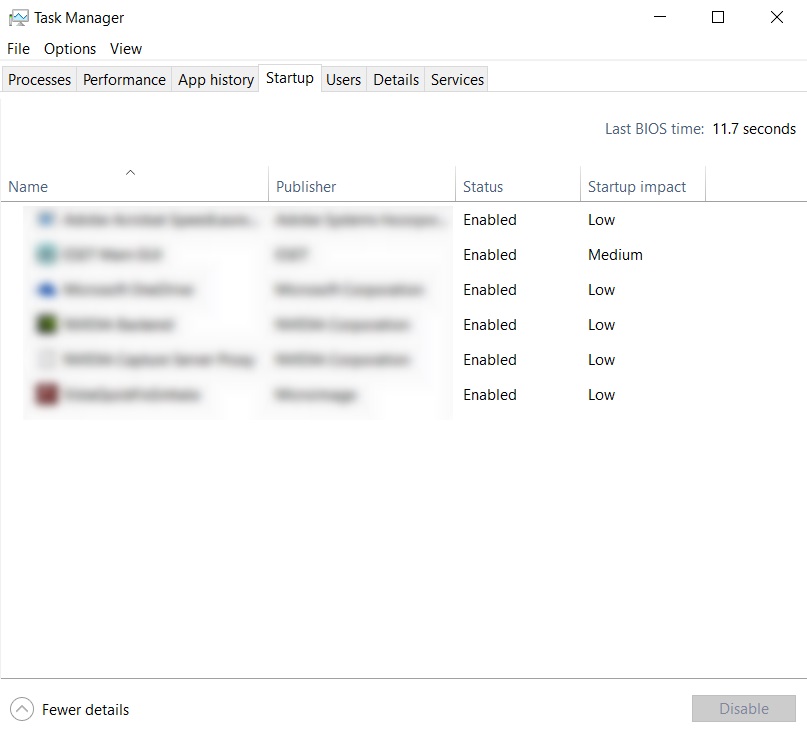
As the name suggests this tab includes every program that starts up when the computer boots up. These programs can be individually sorted out according to your needs. The Startup impact column helps to identify the impact of each program on the computer.
Users
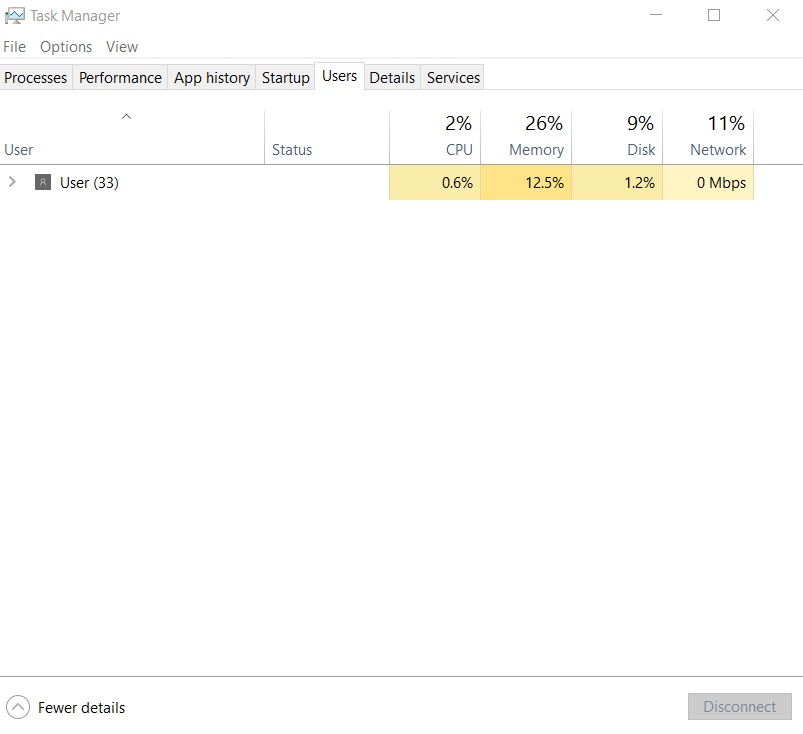
Under this tab, all user accounts that are logged onto the PC are visible and can be managed from here. This is incredibly useful in identifying processes being run by other user accounts.
Details
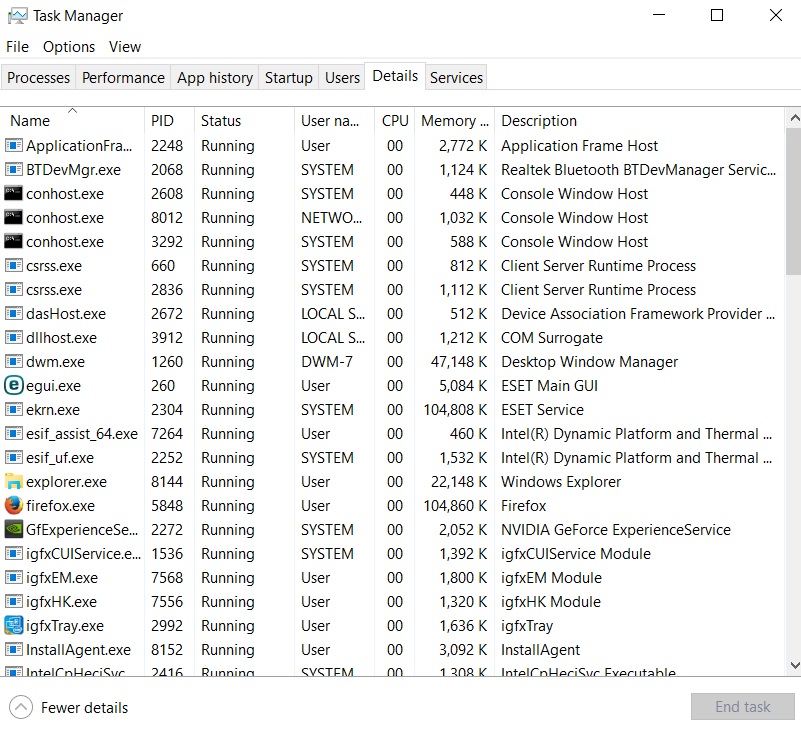
All individual processes that are running at any instance are listed in this tab. This tab is extremely useful for advanced troubleshooting and right-clicking on a process brings up several actions and tools for you to choose from.
Services
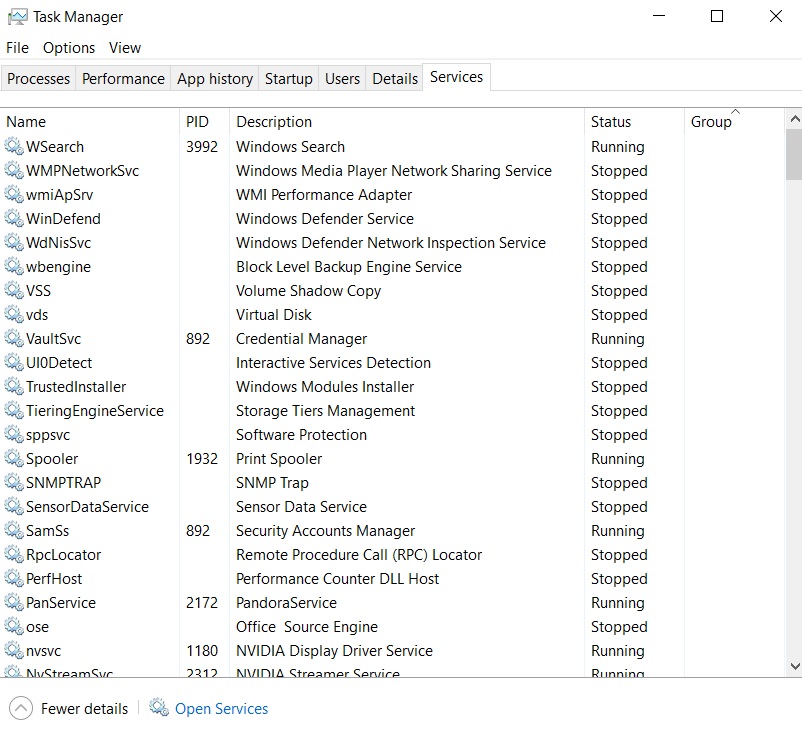
This tab lists all services that are running in the background in a detailed and simple manner. Click the Open Services feature at the bottom to launch the maximized Services tool, which will provide you with a lot more options.
As you can see, the Task Manager is not only about managing the applications that are running at the moment, but it also provides you with handy options to give a massive boost to your computer’s performance by making the right calls.